by Pigeon Patrol | Feb 26, 2020 | 4-S Gel Bird repellent, Animal Deterrent Products, Bird Deterrent Products, Bird Netting, Bird Spike, Bird Spikes, Pigeon Control, Pigeon Droppings, Pigeon Patrol's Services, Pigeon Spikes, Pigeons in the News, UltraSonic Bird Control
What is Bird Fever, Bird Flu, scientifically known as Histoplasmosis, an acute (primary) pulmonary disease
Acute pulmonary histoplasmosis is a respiratory infection that is caused by inhaling the spores of the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum, the fungus that causes histoplasmosis. The infection usually affects the lungs and symptoms can vary greatly. It can sometimes affect other parts of the body, including the eyes, liver, central nervous system, skin, or adrenal glands. For example, “ocular histoplasmosis syndrome” (also known as “presumed ocular histoplasmosis”) is a condition that results in impaired vision (affects the eyes). Having a weakened immune system increases your risk for getting this disease (e.g., the very young, very old, or those with medical conditions that lower the body’s resistance to infections).
This Histoplasma organism thrives in moderate temperatures and moist environments. It is found in the central and eastern United States, eastern Canada, Mexico, Central America, South America, Africa, and Southeast Asia. It is commonly found in the soil in river valleys. It gets into the soil mostly from droppings from chickens, pigeons, starlings, blackbirds, and bats. Birds are not infected with it because of their high body temperatures, but they do carry it on their feathers. Bats can be infected because they have a lower body temperature than birds and can excrete the organism in their droppings.
To multiply, Histoplasma capsulatum produces small spores called conidia. The conidia of Histoplasma capsulatum are only two millionths of a meter (microns, �m) in diameter. When these conidia are inhaled, they are small enough that they enter the lungs and start an infection. Many of these infections are easily overlooked because they either produce mild symptoms or none at all. However, histoplasmosis can be severe and produce an illness similar to tuberculosis.
You can get sick when you breathe in spores that the fungus produces. Every year, thousands of people worldwide are infected, but most do not become seriously sick. Most have no symptoms or have only a mild flu-like illness and recover without any treatment.
Acute pulmonary histoplasmosis may happen as an epidemic, with many people in one region becoming sick at the same time. People with weakened immune systems (see Symptoms section below) are more likely to:
- Get the disease, if exposed to the fungus spores
- Have the disease come back
- Have more symptoms, and more serious symptoms, than others who get the disease.
Risk factors include traveling to or living in the central or eastern United States near the Ohio and Mississippi river valleys, and being exposed to the droppings of birds and bats. This threat is greatest after an old building is torn down, or when exploring caves.
Question: “The town where I live is home to a legion of pigeons, and we have many tales of people getting sick with “bird fever.” I am a teacher, and I work in a very old school. I have seen two very large piles of pigeon droppings in the school’s attic. I am concerned because I work on the floor directly below the attic, the ceiling of my classroom has cracks in it. Also, the school has recently installed a new air conditioning system in the attic. Am I at risk for catching bird fever?”
Answer: The fungus, Histoplasma capsulatum, can be found in pigeon droppings. Infection by H. capsulatum can cause the disease Histoplasmosis. Three fourths of those who are infected with the fungus exhibit no symptoms or show symptoms of influenza (“flu”). One quarter of those who are infected with the fungus exhibit illness of varying severity, and among these the most common illness is a pneumonia of short duration.
Source
At Pigeon Patrol, we manufacture and offer a variety of bird deterrents, ranging from Ultra-flex Bird Spikes with UV protection, Bird Netting, 4-S Gel and the best Ultrasonic and audible sound devices on the market today.
Contact us at 1- 877– 4– NO-BIRD, (604) 585-9279 or visit our website at www.pigeonpatrol.ca
Bird Gone, Pigeon Gone, Seagull Gone, Pigeon issue, pigeon spikes, 1-877-4NO-BIRD, 4-S Gel, Bird Control, Pigeon Control, bird repellent, Bird Spikes, sonic bird repellent, stainless steel bird spikes, bird spikes Vancouver, Ultra Sonic Bird Control, Bird Netting, Plastic Bird Spikes, Canada bird spike deterrents, Pigeon Pests, B Gone Pigeon, Pigeon Patrol, pest controller, pest control operator, pest control technician, Pigeon Control Products, humane pigeon spikes, pigeon deterrents, pigeon traps, Pigeon repellents, Sound & Laser Deterrents, wildlife control, raccoon, skunk, squirrel deterrent, De-Fence Spikes, Dragons Den, Canada bird spikes, Canada pigeon, pigeon control, pigeon patrol, pigeon. Kill pigeons, crow, starling

by Pigeon Patrol | Feb 26, 2020 | 4-S Gel Bird repellent, Animal Deterrent Products, Bird Deterrent Products, Bird Netting, Bird Spike, Bird Spikes, Pigeon Control, Pigeon Droppings, Pigeon Patrol's Services, Pigeon Spikes, Pigeons in the News, UltraSonic Bird Control
How Did the Pigeon Get to NYC? One can scarcely think of any park in NYC — or any city, really — without envisioning the ubiquitous pigeon there as well. Despite signs requesting you not feed the birds in adjacent Bryant Park, the library has more than its share of feathered patrons.
But how did this non-native species become the bird most associated with New York City? Pigeons are certainly not indigenous, but they have made themselves quite at home in the Big Apple. In Wild New York: A Guide to the Wildlife, Wild Places, & Natural Phenomena of New York City, authors Margaret Mittelbach and Michael Crewdson explain “Also called rock doves, pigeons were first brought to this country from Europe, probably during the 1600s, and that their original status here was that of a barnyard animal, raised purely for the table.”
Captive pigeons somehow struck out on their own, nesting easily in the crevices of buildings that are not that different than the cliff sides on which their ancestors dwelled. Over time, pigeons and their young squab dwindle from menus and dinner tables. Ironically, most city pigeons depend exclusively on humans to feed them, whether purposefully or accidentally through litter.
to feed them, whether purposefully or accidentally through litter.
Thousands of years ago in North Africa, people built dovecotes to house and raise pigeons for food and to use their droppings as fertilizers. New Yorkers have kept a similar relationship with pigeons by building coops on building rooftops and raising pigeons for racing and companionship. Bert on Sesame Street famously loves pigeons, enough to sing about it. Scientist Nikola Tesla was extremely fond of pigeons and would frequent NYC parks searching for injured birds, which he would then bring back to his residence at the Hotel New Yorker to nurse them back to health. His obsession with pigeons is documented in the novel The Invention of Everything Else and he had a favorite pigeon, which he mourned when she died.
The New York Times has covered pigeons in abundance and there are many non-fiction titles out there to help you learn more about these birds such as Pigeons: The Fascinating Saga of the World’s Most Revered and Reviled Bird by Andrew D. Blechman. There are pigeon appreciation groups and documentaries by local filmmakers, such as JL Aronson’s Up on the Roof. Pigeons are definitely part of New York’s wildlife and landscape.
Source
At Pigeon Patrol, we manufacture and offer a variety of bird deterrents, ranging from Ultra-flex Bird Spikes with UV protection, Bird Netting, 4-S Gel and the best Ultrasonic and audible sound devices on the market today.
Contact us at 1- 877– 4– NO-BIRD, (604) 585-9279 or visit our website at www.pigeonpatrol.ca
Bird Gone, Pigeon Gone, Seagull Gone, Pigeon issue, pigeon spikes, 1-877-4NO-BIRD, 4-S Gel, Bird Control, Pigeon Control, bird repellent, Bird Spikes, sonic bird repellent, stainless steel bird spikes, bird spikes Vancouver, Ultra Sonic Bird Control, Bird Netting, Plastic Bird Spikes, Canada bird spike deterrents, Pigeon Pests, B Gone Pigeon, Pigeon Patrol, pest controller, pest control operator, pest control technician, Pigeon Control Products, humane pigeon spikes, pigeon deterrents, pigeon traps, Pigeon repellents, Sound & Laser Deterrents, wildlife control, raccoon, skunk, squirrel deterrent, De-Fence Spikes, Dragons Den, Canada bird spikes, Canada pigeon, pigeon control, pigeon patrol, pigeon. Kill pigeons, crow, starling
by Pigeon Patrol | Feb 26, 2020 | 4-S Gel Bird repellent, Animal Deterrent Products, Bird Deterrent Products, Bird Netting, Bird Spike, Bird Spikes, Pigeon Control, Pigeon Droppings, Pigeon Patrol's Services, Pigeon Spikes, Pigeons in the News, UltraSonic Bird Control
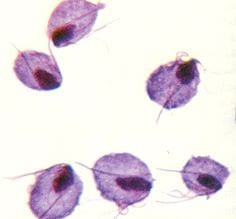
Trichomoniasis: Finding Sick, dying or dead pigeons?
Hello Everyone
We have been getting an increasing number of
Trichomoniasis related calls at this time of year. Every year outbreaks are seen during the late summer and autumn. This disease does not pose a threat to the health of humans, cats or dogs.

Greenfinches are reported most frequently, but potentially any bird can be infected, including pigeons and doves and some birds of prey. The trichomonad parasite lives in the upper digestive tract of the bird, and its actions progressively block the bird’s throat making it unable to swallow food, thus killing it by starvation.
The infection is spread as pigeons feed one another with regurgitated food during the breeding season, and through food and drinking water contaminated with regurgitated saliva. Saliva can also contaminate a birdbath. Trichomoniasis cannot live long outside a hosted pigeons.
Trichomoniasis causes lesions in the throat of the infected pigeons, which makes it progressively harder for the bird to swallow its food, and eventually breathe. Birds will also show signs of lethargy and fluffed up plumage, drooling saliva and regurgitated food. Affected birds frequently have matted wet plumage around the face and beak and uneaten food in and around the beak.
If a number of birds show symptoms, we recommend to stop putting out all food and leave bird baths dry for at least three weeks. This helps to disperse the feeding birds and reduce the contact between sick and healthy individuals, thus slowing down the outbreak. The higher the concentration of birds at a feeding station, the greater the chance of another bird picking up an infected food particle and exposing itself to the infection.
There are also a few other actions you can take to help:
Use feeders with drainage holes to avoid moisture building up
– Use more than one feeding site to reduce the number of birds in one place
– Rotate feeders around several locations to ‘rest’ each spot to prevent build up of infection on the ground underneath.
– Clean and disinfect feeders and water baths regularly, rinsing thoroughly and allowing to air dry completely – this itself will kill some diseases
– Keep the bucket and brush you clean feeders with outside and using just for this purpose
– Sweep up droppings and spilt or old food and disposing of it carefully in an outside bin
– Change the water in baths frequently – ideally daily
– Wash your hands carefully afterwards
No effective treatment can be administered to birds in the wild, because it is impossible to ensure that the infected individuals receive an adequate dose and that healthy birds do not pick up the medicine.
At Pigeon Patrol, we manufacture and offer a variety of bird deterrents, ranging from Ultra-flex Bird Spikes with UV protection, Bird Netting, 4-S Gel and the best Ultrasonic and audible sound devices on the market today.
Contact us at 1- 877– 4– NO-BIRD, (604) 585-9279 or visit our website at www.pigeonpatrol.ca
Bird Gone, Pigeon Gone, Seagull Gone, Pigeon issue, pigeon spikes, 1-877-4NO-BIRD, 4-S Gel, Bird Control, Pigeon Control, bird repellent, Bird Spikes, sonic bird repellent, stainless steel bird spikes, bird spikes Vancouver, Ultra Sonic Bird Control, Bird Netting, Plastic Bird Spikes, Canada bird spike deterrents, Pigeon Pests, B Gone Pigeon, Pigeon Patrol, pest controller, pest control operator, pest control technician, Pigeon Control Products, humane pigeon spikes, pigeon deterrents, pigeon traps, Pigeon repellents, Sound & Laser Deterrents, wildlife control, raccoon, skunk, squirrel deterrent, De-Fence Spikes, Dragons Den, Canada bird spikes, Canada pigeon, pigeon control, pigeon patrol, pigeon. Kill pigeons, crow, starling
by Pigeon Patrol | Feb 26, 2020 | 4-S Gel Bird repellent, Animal Deterrent Products, Bird Deterrent Products, Bird Netting, Bird Spike, Bird Spikes, Pigeon Control, Pigeon Droppings, Pigeon Patrol's Services, Pigeon Spikes, Pigeons in the News, UltraSonic Bird Control
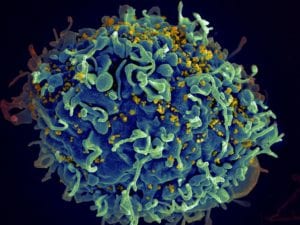
Did The Common Pigeon Bring An AIDS-Defining Fungus To Asia?
New research has shed light on the origins of a fungal infection which is one of the major causes of death from AIDS-related illnesses that pigeon may bring.
AsianScientist (May 4, 2011) – New research has shed light on the origins of a fungal infection which is one of the major causes of death from AIDS-related illnesses. The study, published yesterday in the journal PLoS Pathogens, shows how the more virulent forms of Cryptococcus neoformans evolved and spread out of Africa and into Asia. C. neoformans is a highly pathogenic fungi which causes life-threatening infections in immunocompromised humans.
The fungus mainly lives in decaying pigeon or chicken droppings and enters the human host through the respiratory tract. The spores spread to extrapulmonary tissues and the central nervous system where it causes meningitis. A particularly virulent form, C. neoformans variety grubii (Cng), is a major cause of death among HIV-AIDS infected patients.
Up to 1 million cases of cryptococcal meningitis that result in over 600,000 deaths are reported each year. Cryptococcal meningitis affects nearly 20 percent of HIV-AIDS patients in Thailand, where HIV-AIDS is an emerging epidemic.
Researchers from the U.K., Netherlands, and Naresuan University in Thailand took 183 clinical samples in Thailand and compared them with the global database of 77 isolates. Genetic sequencing revealed that the Thailand samples taken from 11 provinces were highly homogenous. In comparison with the rest of the world’s population of Cng, specifically Africa where most of the lineages are found, the strains in Thailand had significantly less genetic diversity.
Analyses on the origin of Thailand’s strain dated it back to an ancestral African population diverging within the last 7,000 years. The common pigeon, domesticated 5,000 years ago, is thought to have spread the pathogen through its excrements when it was introduced to Europe. Subsequent voyages from Europe to Asia 500 years ago may have allowed Cng to broaden its ecological range.
The article can be found at: Simwami SP et al. (2011) Low Diversity Cryptococcus neoformans Variety grubii Multilocus Sequence Types from Thailand Are Consistent with an Ancestral African Origin. ——
Source: Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council.
At Pigeon Patrol, we manufacture and offer a variety of bird deterrents, ranging from Ultra-flex Bird Spikes with UV protection, Bird Netting, 4-S Gel and the best Ultrasonic and audible sound devices on the market today.
Contact us at 1- 877– 4– NO-BIRD, (604) 585-9279 or visit our website at www.pigeonpatrol.ca
Bird Gone, Pigeon Gone, Seagull Gone, Pigeon issue, pigeon spikes, 1-877-4NO-BIRD, 4-S Gel, Bird Control, Pigeon Control, bird repellent, Bird Spikes, sonic bird repellent, stainless steel bird spikes, bird spikes Vancouver, Ultra Sonic Bird Control, Bird Netting, Plastic Bird Spikes, Canada bird spike deterrents, Pigeon Pests, B Gone Pigeon, Pigeon Patrol, pest controller, pest control operator, pest control technician, Pigeon Control Products, humane pigeon spikes, pigeon deterrents, pigeon traps, Pigeon repellents, Sound & Laser Deterrents, wildlife control, raccoon, skunk, squirrel deterrent, De-Fence Spikes, Dragons Den, Canada bird spikes, Canada pigeon, pigeon control, pigeon patrol, pigeon. Kill pigeons, crow, starling
by Pigeon Patrol | Feb 26, 2020 | 4-S Gel Bird repellent, Animal Deterrent Products, Bird Deterrent Products, Bird Netting, Bird Spike, Bird Spikes, Pigeon Control, Pigeon Droppings, Pigeon Patrol's Services, Pigeon Spikes, Pigeons in the News, UltraSonic Bird Control
A new virus has been isolated from the tissues of pigeons with visceral lesions that were characterized by focal necrosis of parenchymatous tissue, by the presence in affected cells of

intranuclear inclusions of the herpetic type, and by secondary inflammatory reaction. This newly recognized virus, which has been tentatively called the I.N.I. agent is pathogenic for pigeons and embryonated eggs but is avirulent for rabbits, guinea pigs, and mice. The virus is smaller than the agent of psittacosis and is immunologically different from it. The I.N.I. agent and psittacosis virus were both of etiological importance in an epizootic among pigeons. Some birds were infected simultaneously with the two agents while others were infected with only one.
Source
At Pigeon Patrol, we manufacture and offer a variety of bird deterrents, ranging from Ultra-flex Bird Spikes with UV protection, Bird Netting, 4-S Gel and the best Ultrasonic and audible sound devices on the market today.
Contact us at 1- 877– 4– NO-BIRD, (604) 585-9279 or visit our website at www.pigeonpatrol.ca
Bird Gone, Pigeon Gone, Seagull Gone, Pigeon issue, pigeon spikes, 1-877-4NO-BIRD, 4-S Gel, Bird Control, Pigeon Control, bird repellent, Bird Spikes, sonic bird repellent, stainless steel bird spikes, bird spikes Vancouver, Ultra Sonic Bird Control, Bird Netting, Plastic Bird Spikes, Canada bird spike deterrents, Pigeon Pests, B Gone Pigeon, Pigeon Patrol, pest controller, pest control operator, pest control technician, Pigeon Control Products, humane pigeon spikes, pigeon deterrents, pigeon traps, Pigeon repellents, Sound & Laser Deterrents, wildlife control, raccoon, skunk, squirrel deterrent, De-Fence Spikes, Dragons Den, Canada bird spikes, Canada pigeon, pigeon control, pigeon patrol, pigeon. Kill pigeons, crow, starling

by Pigeon Patrol | Feb 26, 2020 | Animal Deterrent Products, Bird Deterrent Products, Bird Netting, Pigeon Control, Pigeon Droppings, Pigeon Patrol's Services, Pigeon Spikes, Pigeons in the News, UltraSonic Bird Control
I saw a fat pigeon the other day. There it was, doddering about on a Bowery doorstep, looking all smug and content. The fat pigeon had a fat pigeon ass and a fat pigeon belly that spanned the width of two normal birds, and I tried to imagine how the fat pigeon got to be so big. I pictured the fat pigeon tearing into a Big Mac, tufts of all-beef patty and sesame bun flying into the air with every peck, until the fat pigeon’s face was smeared with special sauce. I imagined the fat pigeon annihilating a holster of spilled French fries, and to be honest the thought of it got me pissed. Fries are for people, not pigeons. I stared at the fat pigeon long and hard, and the fat pigeon stared at me.
I’m not the only one who’s been seeing fat pigeons. In 2007, fat pigeons swarmed into Liverpool, England, pecking and pooping and plodding about, and so upset the locals that the City Council brought in 10 robotic peregrine falcons to scare off the zaftig varmints. A high-fat, garbage-based junk food diet had given the pigeons “a scruffy, unhealthy appearance,” explained one city official. Everyone agreed the fat pigeons had to go.
Of course, fat pigeons may be only the beginning. If one embarks on a tour of animal corpulence, spiraling out from captivity to the wild, a seemingly growing army of rotund beasts rounds into view. At home the fat animals are well known: They are fat husbands and fat children, fat dogs, fat cats, and fat pet macaws. Zoos and aquariums keep their own set of fat creatures in captivity. In 2008, for example, the dolphins at Japan’s Kinosaki Marine World grew too plump to jump, and were placed on a reduced-mackerel diet. A similar difficulty arose in a Shanghai aquarium when the sharks got so tubby that keepers gave them fish stuffed with cabbage to help them slim down.
Out in the country, some free-range fatties have sauntered onto the scene. Horse obesity is a growing concern on farms. In Arizona, wild burros have ballooned into genuine fat asses thanks to carrot-proffering tourists. The Lake Tahoe area’s garbage-eating black bears are unusually paunchy. And then there are the rats. Are the rats fat? One scientific study in 2010 found that feral rats collected near Baltimore had grown heavier over time. According to conventional wisdom, “wild” animals do not get fat. But is that truism breaking down for the commensal animals—like pizza-scarfing squirrels—that live in and around our fat- and sugar-laden “toxic” food environment? Has the obesity epidemic escaped from captivity? Is the Age of Fat Pigeons nigh?
Obesity researcher David Allison was on the team that identified the chunky urban rats. He and his colleagues also found signs of weight gain among captive populations of macaques, chimpanzees, vervets, marmosets, dogs, cats, and mice. For their study of vermin in the field, they reanalyzed weight data from rats captured in Baltimore alleyways as well as from rural rats trapped on parklands and farms between 1948 and 2006. The city rats had porked up more than the country rats, but both groups had probably needed to widen their burrows. I interviewed other rat experts who agreed that city rats tend to be huskier than their wild siblings, which subsist on bugs, slugs, acorns, and one another instead of half-eaten bagels and chicken wings. (Laboratory rats, with no room to exercise and all-you-can-eat feeding schedules, are bigger still.)
Allison says he doesn’t know why Baltimore’s rats have grown so large. (He doesn’t know for sure they have gotten fatter, as opposed to bigger overall, since his study only looked at weight.) It could be the result of the well-documented increase in food garbage, the selective killing of small rats by predators such as cats, changes in light exposure, improvements in rat health (perhaps facilitated by the food supply), or some environmental toxin that is disrupting the rats’ hormonal systems. Increasing temperatures might be another cause of rodent corpulence. A rat that spends less time shivering in the cold expends less energy. Scientists in Colorado report that shorter winters have given yellow-bellied marmots more time to forage and fill up their yellow bellies. (Climate change can work in the other direction, too: Sheep in the Scottish isles are thought to be getting smaller in the heat.) What about pigeons? Did Allison think the Age of Fat Pigeons was upon us? “[I]t would not at all surprise me if pigeons are more obese or fat than they used to be,” he said.
Different animals respond to calorie surpluses in different ways. Some species experience what biologists call “indeterminate growth” until late in their lives: As the animal takes in more food, it just gets bigger and bigger rather than storing excess calories as fat. Indeterminate growth is common among invertebrates such as earthworms and silverfish, but some mammals do it, too. A study from last year on crop-raiding African elephants showed that the well-nourished bulls got taller and longer and stronger and heavier than their pachyderm peers. All that extra food turned into pure tusker beefcake.
Humans, of course, stop growing in adulthood, so excess calories are converted to love handles under the right conditions. Baboons are the same way. Duke biologist Susan Alberts studied a group that lived near a tourist lodge in Kenya, and got most of its food by plundering a garbage dump instead of wandering the African plains. Not only did some of the animals get flabby as a result, she says, but they got dental cavities, too, and developed the sorts of insulin and cholesterol problems you’d see in a human case of metabolic syndrome. The scientists determined that the baboons weren’t getting sick from excess food—they took in the same number of calories as their wild-roaming brethren, despite a diet of discarded cake and pineapples—but rather they suffered from a lack of exercise. They did start having tons of healthy babies, though; increased fertility is the typical biological response to a surplus of food. The fat baboons are no longer being closely monitored, because the area where they hang out is patrolled by too many cantankerous wild buffaloes.
What did Alberts have to say about my fat pigeon? Did she think the global population of fat animals had reached an all-time high? She wasn’t sure. “If you went back to Egypt 5,000 years ago where they had lots of grain stored in granaries you can bet they had fat cats and fat mice and fat dogs.” But, she noted, “[W]herever there is excess human food, and humans have commensals, those commensals are going to be able to get fat.”
It might seem that birds shouldn’t get fat because they have to fly, but that is not the case. Many migratory birds get supremely blubbery in the days leading up to their big trip—some to 70 percent body fat. Adipose tissue weighs less than muscle, but it carries more energy, making it an essential resource for a long-distance flight. Pigeons don’t migrate, though, and despite their seasonal weight gain, birds tend not to be among the world’s top fatties. Research by the British zoologist Caroline Pond, author of The Fats of Life, suggests that human beings are among the bigger lard-asses in the animal kingdom, neck in neck with notable porkers like the hedgehog, the polar bear and the great whales, the fattest of God’s creatures. (The whole point of whaling was to get at their lipids.) In general carnivores tend to be more prone to growing chubby, as fatness is an adaptation to an unpredictable food supply.
Pond may be the world’s leading scholar of fat animals. Beginning in the early 1980s, she began riding her bike around the woodlands near her U.K. home at night collecting all the road kill she could carry: hedgehogs, badgers, foxes, whatever turned up stiff. Zookeepers and farmers gave her corpses, too—camels, monkeys, brown bears, whales—and soon she had dissected more than 250 mammals. Her interest was the comparative distribution of adipose tissue, a topic most life scientists at the time were too dignified to tackle. In mammals fat depots surround most organs, but textbooks often showed them with the fat removed, as if it were not part of the biological picture. What did Pond think about my fat-pigeon investigation? How was she preparing for the Age of Fat Pigeons? Well, she didn’t really think pigeons got fat.
Pigeon experts agree. Courtney Humphries, author of the book Superdove: How the Pigeon Took Manhattan … and the World, said she hadn’t heard of a pigeon obesity epidemic. Daniel Sol, a pigeon researcher in Spain, brought my fat pigeon flight of fancy crashing to Earth in an email: “Even in captivity, where food is not limiting, feral pigeons do not tend to get fat.” He said Montreal pigeons are bigger than Barcelona pigeons, even though Montreal pigeons have less food. He guessed the difference was due to the Canadian cold. Karen Purcell with Cornell’s Project PigeonWatch suggested the fat pigeon I saw might have been fluffing out its feathers because it was chilly. Urban bird expert John Marzluff wondered if the fat pigeon I saw might have been a dominant male—a big stud. He did allow that my vision of the fat pigeon eating a Big Mac was not crazy, based on his work in crows. “Oh, they love Big Macs, French fries and Cheetos and hot dogs. Corn dogs are especially a favorite.” But urban birds don’t seem to get fat. Too many hawks and other birds to worry about. As the animal philosopher Rikki-Tikki-Tavi once observed, “a full meal makes a slow mongoose.”
So my fat pigeon was a phantom. The obesity epidemic had not escaped captivity—it had colonized my mind. And if I ever see that pigeon again, I know what I will say: It was wrong of me to call you fat.
Source
At Pigeon Patrol, we manufacture and offer a variety of bird deterrents, ranging from Ultra-flex Bird Spikes with UV protection, Bird Netting, 4-S Gel and the best Ultrasonic and audible sound devices on the market today.
Contact us at 1- 877– 4– NO-BIRD, (604) 585-9279 or visit our website at www.pigeonpatrol.ca
Bird Gone, Pigeon Gone, Seagull Gone, Pigeon issue, pigeon spikes, 1-877-4NO-BIRD, 4-S Gel, Bird Control, Pigeon Control, bird repellent, Bird Spikes, sonic bird repellent, stainless steel bird spikes, bird spikes Vancouver, Ultra Sonic Bird Control, Bird Netting, Plastic Bird Spikes, Canada bird spike deterrents, Pigeon Pests, B Gone Pigeon, Pigeon Patrol, pest controller, pest control operator, pest control technician, Pigeon Control Products, humane pigeon spikes, pigeon deterrents, pigeon traps, Pigeon repellents, Sound & Laser Deterrents, wildlife control, raccoon, skunk, squirrel deterrent, De-Fence Spikes, Dragons Den, Canada bird spikes, Canada pigeon, pigeon control, pigeon patrol, pigeon. Kill pigeons, crow, starling





