
by Pigeon Patrol | Feb 9, 2021 | Bird Law, Bird Netting, Bird Spike, Bird Spikes, Columbidae, Pigeon Patrol's Services, Pigeon Spikes
If you’re looking for the answer to the question “do anti bird spikes reduce pest bird problems?”, then you undoubtedly already have a problem with bird control. Birds are either landing or nesting on your property.
So lets see if bird spikes really work!
You need to look at why the birds are landing and possibly building a nest. Is it because you feed wild birds and other unwelcome species, such as feral pigeons or starlings, are having the lion’s share? Birds go to places where food is most abundant and easy to take. If you want to control what birds you attract to your garden, especially smaller ones, but not pigeons and starlings, make sure you only place food in feeding containers that make it virtually impossible for the larger birds to feed from. If there’s no readily available food, these larger birds will move on to somewhere else.
Secondly, if you have a bird control problem with the smaller birds then anti-bird spikes may not be effective in preventing them from landing and nesting. If you think about it logically, the smaller birds have feet which are designed to grab hold of small branches and twigs – spikes can give them this ideal landing perch.
However, larger birds, such as seagulls and pigeons don’t have feet adapted for landing on fine spiky branches and twigs and therefore anti bird spikes can be a very effective deterrent. If there are a vast numbers of birds, their droppings have been known to build-up on and around the spikes which then forms an ideal platform for them to build nests. SOURCE
Conclusion:
Anti-bird spikes can reduce pest bird control problems if you’re trying to humanely deter larger birds from landing or nesting. On the other hand, the spikes may be the ideal conditions for smaller birds; so you need to take a multi-faceted approach to control unwanted birds from making your property their home or landing site.
Do bird spikes hurt the birds? Bird and pigeon spikes do not hurt birds, they act as a visual and physical barrier. Bird spikes are a humane bird deterrent as the bird doesn’t come into direct contact with the bird spikes.
Pigeon Patrol Products & Services is the leading manufacturer and distributor of bird deterrent (control) products in Canada. Pigeon Patrol products have solved pest bird problems in industrial, commercial, and residential settings since 2000, by using safe and humane bird deterrents with only bird and animal friendly solutions. At Pigeon Patrol, we manufacture and offer a variety of bird deterrents, ranging from Ultra-flex Bird Spikes with UV protection, Bird Netting, 4-S Gel and the best Ultrasonic and audible sound devices on the market today.
Contact us at 1- 877– 4– NO-BIRD, (604) 585-9279 or visit our website at www.pigeonpatrol.ca
Pigeon / Pigeon Patrol / Pigeons Roosting / Vancouver Pigeon Patrol / Bird Control / Surrey Pigeon Control / Pest / Vancouver Pigeon Blog / Birds Inside Home / Pigeons in the cities / Ice Pigeons/ What to do about pigeons/ most common types of sparrows , Damages Caused by Sparrows, How To Keep Raccoons Away, Why Are Raccoons Considered Pests?de-fence, Pigeon Nesting and Breeding Patterns and Behavior What Do I Do With a Bird Trapped in My Wall? Professional Bird Control Company Keep The Birds Away From Your Business Why Are Raccoons Considered Pests? BIRD SPIKES WORK 
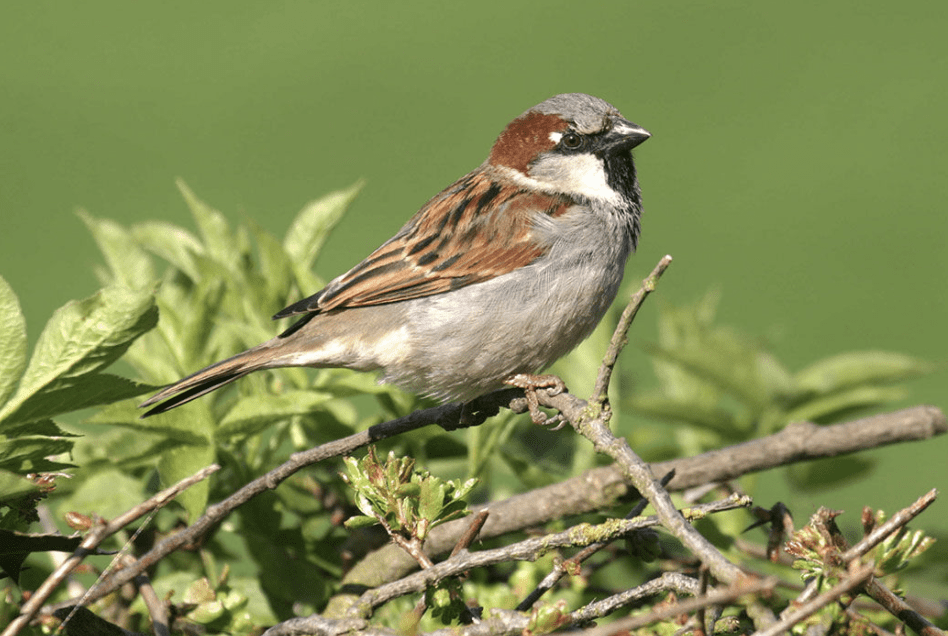
by Pigeon Patrol | Dec 7, 2020 | Animal Deterrent Products, Bird Deterrent Products, Bird Netting, Pigeon Patrol's Services, Pigeon Spikes, Pigeons in the News, UltraSonic Bird Control
Looking to learn more about sparrows? Keep on reading to find out 10 sparrow facts!/am-tree-sparrow-58ca9fc73df78c3c4f9a3610-5a0e0f3a9e942700377f9e72.jpg)
Sparrow is a species of small Passerine birds, also acknowledged as True sparrows or Old world Sparrows. It originates from North Africa and is also found in Asia, Australia, Europe, New Zealand and North America. Sparrows cannot be found in forests or deserts, unlike other birds. It prefers being in close association to human settlement, including urban and rural areas. They inhabit on ideal sparrow habitat nesting on buildings, roofs, and houses.
Sparrows are brown-grey chubby birds. They have short tails with stubby and powerful beaks. These are effortless flying birds with small size and bodies. These creatures make their way to the air creating a splendid sight to see. Sparrows are considered to be extreme vocal birds of all times. The sizes of these birds vary according to the region they inhabit. Sparrows are similar to other seed-eating birds except they possess an extra bone in tongue and an outer primary feather. On the other hand, cheeky sparrows have a diverse range of colors varying from sandy blonde to a rich red color. source
10 Sparrow Facts
- Sparrows have both genders males and females which can be easily distinguished by feather coloration. Females possess brown backs with stripes while males possess reddish backs and black bibs.
- Sparrows are said to be the social creatures. They live in colonies which are commonly mentioned to as flocks.
- Sparrows are primarily carnivorous by nature i.e. they are meat eaters. They learn to change their eating habit more frequently while they live in close association with Sparrows primarily eat moths and also feed on small insects. They can also feed on seeds, fruits, and berries.
- Sparrows easily adapt to the life in human settlements due to the constant supply of food. These creatures learn to eat food which they are provided by the people when people build their bird feeders.
- They usually fly at the speed of about 24 miles per hour, in the case of emergency they can speed up to 31 miles per hour.
- Although sparrows are not considered as water birds, they swim at a very fast pace to escape from predators.
- Predators of sparrows are usually dogs, cats, foxes and snakes. The young new ones are an easy target for these carnivores.
- Sparrows are not included in territorial animals, but they are aggressively protective about their nests from other sparrows.
- Sparrow is considered to be a very small Its length can vary between 4-8 inches and weighs around 0.8 to 1.4 ounces. With such small bodies, they can easily fit into the small openings.
- It possesses a stout body with rounded wings. Its body is covered with brown, black and white feathers.
About Pigeon Patrol:
Pigeon Patrol Products & Services is the leading manufacturer and distributor of bird deterrent (control) products in Canada. Pigeon Patrol products have solved pest bird problems in industrial, commercial, and residential settings since 2000, by using safe and humane bird deterrents with only bird and animal friendly solutions. At Pigeon Patrol, we manufacture and offer a variety of bird deterrents, ranging from Ultra-flex Bird Spikes with UV protection, Bird Netting, 4-S Gel and the best Ultrasonic and audible sound devices on the market today.
Contact us at 1- 877– 4– NO-BIRD, (604) 585-9279 or visit our website at www.pigeonpatrol.ca
Pigeon / Pigeon Patrol / Pigeons Roosting / Vancouver Pigeon Patrol / Bird Control / Surrey Pigeon Control / Pest / Vancouver Pigeon Blog / Birds Inside Home / Pigeons in the cities / Ice Pigeons/ What to do about pigeons/ most common types of sparrows
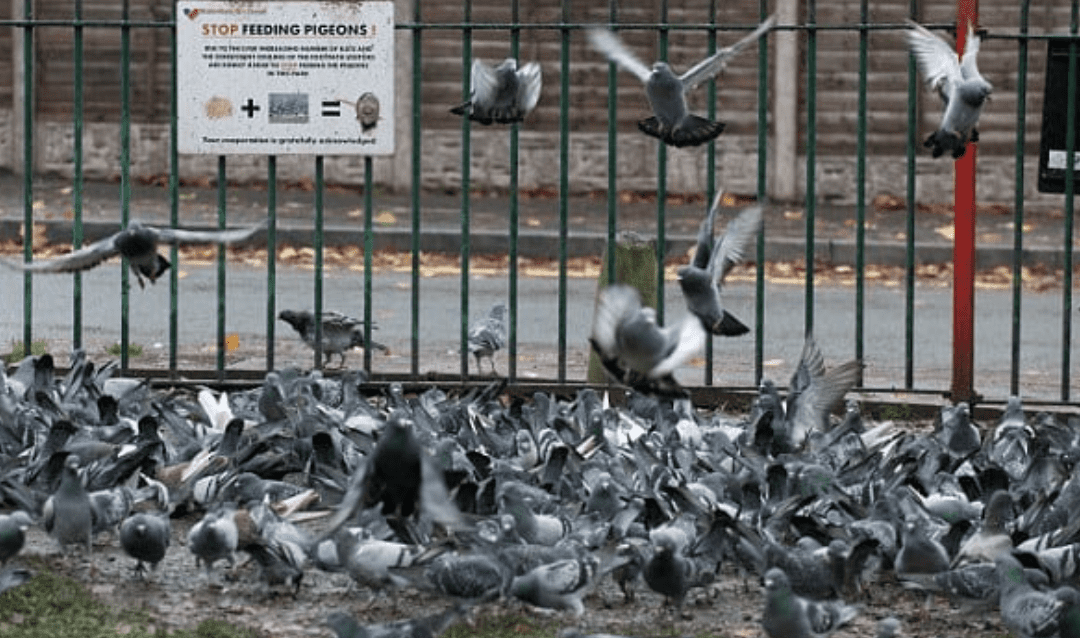

by Pigeon Patrol | Nov 29, 2020 | Bird Deterrent Products, Pigeon Patrol's Services, Pigeon Spikes, Pigeons in the News
Having bird problems? Keep on reading to find out things you can do to get rid of them!
From a pigeon’s perspective, city living can’t be beat. Food and water are readily available. Predators are rare. Plus, there’s plenty of free housing. Pigeons find our window ledges, rooftops, bridges, and warehouses to be ideal substitutes for the natural ledges in cliff sides that they have always used as roosting, nesting, and sheltering sites.
When flocks grow too large and become a nuisance, killing the birds is often the first plan of action. But killing pigeons doesn’t work, and there are better, non-lethal ways to fix a pigeon problem.

Steps to Solve Some Pigeon Problems
You may just need one or a combination of all three techniques, depending on the size of the pigeon population you’re dealing with.
Stop feeding the pigeons (intentionally or not)
Most conflicts with pigeons can be tied at one point or another to feeding, intentionally or otherwise.
Pigeons get fed plenty of handouts and garbage, but there are also well-intentioned pigeon lovers who regularly feed the birds. This does the pigeons more harm than good as the pigeons begin to gather in large numbers, often leading to inhumane and ineffective attempts to reduce their numbers.
When such troubles arise, the best thing for the birds is to reduce feeding gradually over several weeks. The flock will gradually disperse until the remaining number of birds matches what the area can naturally support.
Unintentional food sources
Even when not feeding on purpose, we humans are messy, leaving leftovers and dropped crumbs everywhere. Pigeons hang around town squares, public parks, and other trafficked areas to help themselves to what we leave behind, especially when convenient roosting and nesting sites are nearby. To discourage pigeons from gathering, food attractants need to be cleaned up regularly.
In suburban neighborhoods, too, homeowners may mistakenly feed pigeons or they may be providing food for pigeons inadvertently when feeding their backyard birds by tossing seed on the ground, rather than putting it in birdfeeders. To discourage pigeons visiting your yard, change the type, amount, and timing of feeding. If most of the pigeons fail to move elsewhere, you’ll need to stop feeding all birds for a couple weeks. (Don’t worry; the birds won’t starve.) When you resume feeding, only put out seed in birdfeeders and keep the ground below them cleaned up.
Prevent roosting and nesting
Pigeons look for flat surfaces for roosting and nesting. Encourage them to do these things elsewhere by making flat surfaces unavailable to them. With the correct application of the right product, roosting structures can be rendered virtually pigeon-free.
Call Pigeon Patrol today to get your bird spikes and netting material to keep pigeons off your property Source
Bird Sound Repellent
The Ultrasonic Impact series are the best bird and animal deterrent systems on the market today.
This perfect unit, offers frequency ranges from 8 kHz to 24 kHz offering 13 different settings.
The TubeSonic emits over 100 natural recorded predator, urban, human, bird /animal distress calls and other environment sounds designed to startle, confuse, disorient, and intimidate pesky birds or animals.
About Pigeon Patrol:
Pigeon Patrol Products & Services is the leading manufacturer and distributor of bird deterrent (control) products in Canada. Pigeon Patrol products have solved pest bird problems in industrial, commercial, and residential settings since 2000, by using safe and humane bird deterrents with only bird and animal friendly solutions. At Pigeon Patrol, we manufacture and offer a variety of bird deterrents, ranging from Ultra-flex Bird Spikes with UV protection, Bird Netting, 4-S Gel and the best Ultrasonic and audible sound devices on the market today.
Contact us at 1- 877– 4– NO-BIRD, (604) 585-9279 or visit our website at www.pigeonpatrol.ca
Pigeon / Pigeon Patrol / Pigeons Roosting / Vancouver Pigeon Patrol / Bird Control / Surrey Pigeon Control / Pest / Vancouver Pigeon Blog / Birds Inside Home / Pigeons in the cities / Ice Pigeons/ What to do about pigeons

by Pigeon Patrol | Nov 29, 2020 | 4-S Gel Bird repellent, Animal Deterrent Products, Bird Deterrent Products, Bird Netting, Pigeon Patrol's Services, Pigeon Spikes, Pigeons in the News, UltraSonic Bird Control
Ever heard of the bird flu? Keep on reading to find out more about what it is!
So what is the bird flu?
The Bird Flu also known as the Avian influenza refers to the disease caused by infection with avian (bird) influenza (flu) Type A viruses. These viruses occur naturally among wild aquatic birds worldwide and can infect domestic poultry and other bird and animal species
When was the bird flu?
The year 2005 has been dubbed ‘the year of bird flu’. Across the globe, the fear of avian influenza has caused government officials to place a higher priority on developing plans to deal with pandemic influenza. A survey published on 23 December 2005 by the World Health Organization (WHO) named avian influenza as the number one health concern. This heightened concern exists despite any evidence suggesting sustained human-to-human transmission of the potentially pandemic H5N1 strain of avian influenza virus. Experts have been closely monitoring occurrences of H5N1 since it first appeared in 1996 in the Chinese province of Guangdong.
The number of confirmed human H5N1 infections doubled in 2005. Of the 142 cases of human H5N1 influenza reported as of 30 December 2005, over half have been fatal. That statistic sparked a media frenzy that H5N1 may develop into the next pandemic strain of influenza. A serological survey published in the Journal of Infectious Disease by Bridges et al. (185, 1005–1010, 2002) showed that although the incidence of human H5N1 infection might be higher than previously thought, the mortality rate might be much lower. Up to 10% of 1,525 asymptomatic poultry workers had antibodies to the H5N1 virus. Most of these human cases are thought to have developed after contact with infected animals. Documented reports suggest that H5N1 can infect many bird species and mammals, in addition to humans. Although more serological studies in affected areas are needed, the 2002 study suggests the virus can infect humans without producing the extreme mortality commonly associated with the H5N1 strain. Yet the fear remains that mutation or reassortment of viral genomic segments with those of other endemic strains of influenza might result in a highly virulent human virus.
The WHO, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization have established extensive surveillance and reporting programs for H5N1 influenza. The year 2005 witnessed an explosion of H5N1 outbreaks in poultry and migrating wild bird populations in Asia, spreading to Russia and eastern Europe. That dissemination occurred despite massive vaccine inoculation programs for poultry initiated by local governments in Asia and culling of infected bird flocks elsewhere. Although not yet reported, experts have expressed concern over the appearance of H5N1 in Africa, where surveillance and control measures are subject to regional conflicts, thereby heightening the risk that a highly transmissible human form of H5N1 virus might evolve. Thus, a race against time is now on to develop and generate effective human vaccines to prevent H5N1 infection and to produce sufficient amounts of antiviral drugs that might lessen disease severity. Therapies aimed at controlling innate immune responses should also be pursued, given the clinical evidence that H5N1 elicits ‘cytokine storms’ that can contribute to disease pathogenesis.
Is all the news dire? No. In fact, the present threat of pandemic influenza has spurred several encouraging steps. There seems to be greater accountability in disease surveillance by local health authorities, who supply critical field samples to international agencies that constitute the WHO Influenza Surveillance Network. The WHO has established several laboratories dedicated to analyzing new isolates of influenza virus, thereby providing much-needed standardized epidemiological information on viral samples obtained from geographically separate regions and monitoring how the virus is evolving from earlier isolates. Should a pandemic strain of human influenza arise, these laboratories can quickly identify the relevant ‘genomic fingerprint’ and advise vaccine manufacturers.
Another welcome consequence of the focus on avian influenza has been a resurgence of interest in vaccine manufacturing. Because which H5N1 influenza isolate will have the ‘right’ combination of mutations that allows it to spread quickly throughout human populations cannot be predicted in advance, vaccine manufacturers need to develop new means for rapid production of effective vaccines. At present, methods for the production of influenza vaccines require billions of chicken eggs, a resource that might be unavailable given the lethality of the virus in avian species. The use of reverse genetics in vaccine design as well as mass production using vaccine-certified cell lines hold the promise of streamlining production schedules and reducing potential bottlenecks based on the availability of eggs. The WHO and the US National Institutes of Health have several recombinant H5N1 prototype vaccine strains derived by reverse genetics from viral isolates from southeast Asia. Both agencies have provided these clones to licensed manufacturers for the development and testing of vaccines, some of which have already entered clinical trials. Governmental licensing agencies need to expedite their review process for vaccines produced by cell-based manufacturing methods. Sufficient incentives or collaborative partnerships must be extended to vaccine manufacturers to retool their production facilities so they can meet the global demand for viral vaccines.
Yet planning for the possibility of a future pandemic must also be done on the local level. As witnessed by the SARS outbreak in 2003, substantial economic consequences can result from the mere threat of a highly transmissible disease. It is imperative that local governments, businesses and other institutions develop and test contingency plans that can be deployed in their communities should a pandemic strain arise. Such contingency plans should be independent of vaccination programs (vaccination with the present viral formulations should be encouraged) or antiviral prophylaxis for exposed people, as no guarantee can be made that sufficient supplies of such agents would be available. These plans should include infection-control measures, identification of essential personnel and possible alternative work procedures (such as telecommuting), and a means of communication to rapidly disseminate critical information. All community members should be educated on the specifics of their plan and what to do in the event of such a health emergency. Such planning might avoid future revisionists from proclaiming 2006 as the year of bird flu. Source

The virus continued to kill chickens and to occasionally infect and sometimes kill people. But as the years passed, the number of human H5N1 cases subsided. There has not been a single H5N1 human infection detected since February 2017. This is the good news
About Pigeon Patrol:
Pigeon Patrol Products & Services is the leading manufacturer and distributor of bird deterrent (control) products in Canada. Pigeon Patrol products have solved pest bird problems in industrial, commercial, and residential settings since 2000, by using safe and humane bird deterrents with only bird and animal friendly solutions. At Pigeon Patrol, we manufacture and offer a variety of bird deterrents, ranging from Ultra-flex Bird Spikes with UV protection, Bird Netting, 4-S Gel and the best Ultrasonic and audible sound devices on the market today.
Contact us at 1- 877– 4– NO-BIRD, (604) 585-9279 or visit our website at www.pigeonpatrol.ca
Pigeon / Pigeon Patrol / Pigeons Roosting / Vancouver Pigeon Patrol / Bird Control / Surrey Pigeon Control / Pest / Vancouver Pigeon Blog / Birds Inside Home / Pigeons in the cities / Ice Pigeons

by Pigeon Patrol | Nov 28, 2020 | Bird Netting, Pigeon Patrol's Services, Pigeon Spikes, Pigeons in the News
Ever wondered why pigeons fly in circles? Keep on reading to find out why!
Why Pigeons Fly In Circles
Pigeons fly in circles to better navigate. These birds have a great sense of smell which they use to navigate. They fly in circles to locate the smell that reminds them of home. They could also be flying in a thermal, these help them look for food and conserve energy when flying.
Pigeons can be weird sometimes. The fact that these birds live close to humans, gives us the privilege to study and learn about their many animal behaviours.
You may have seen a flock of pigeons fly in circles and wonder what’s going on. Well, you are not alone. A lot of humans with an interest in birds have also been baffled by this.
Source
The good news is, thanks to countless scientific research and studies, the reason for this bird phenomenon has been cracked.
This article carefully explains why pigeons and a few other birds fly in circles. We hope it answers your questions.
Pigeons fly in circles to find their way around. These birds are gifted with a strong and acute sense of smell. We humans use our eyes to find our way home, pigeons use their sense of smell to locate their destination.
Flying in circles allows pigeons to sense the earth’s magnetic field and smell the many odours in the air. They do this until they find the smell native to their home.
Another possible reason why pigeons fly in circles is to discourage raptors from preying on them. Pigeons live in the same environment as crows and peregrine hawks, and they sometimes fall prey to these birds.
When a flock of pigeon senses danger from one of these birds, they are likely to leave their area of rest and fly in circles till the threat passes.
Without their sense of smell, these birds would literally be lost. But pigeons aren’t the only birds that fly in circles, many birds fly in circles for various reasons.
About Pigeon Patrol:
Pigeon Patrol Products & Services is the leading manufacturer and distributor of bird deterrent (control) products in Canada. Pigeon Patrol products have solved pest bird problems in industrial, commercial, and residential settings since 2000, by using safe and humane bird deterrents with only bird and animal friendly solutions. At Pigeon Patrol, we manufacture and offer a variety of bird deterrents, ranging from Ultra-flex Bird Spikes with UV protection, Bird Netting, 4-S Gel and the best Ultrasonic and audible sound devices on the market today.
Contact us at 1- 877– 4– NO-BIRD, (604) 585-9279 or visit our website at www.pigeonpatrol.ca
Pigeon / Pigeon Patrol / Pigeons Roosting / Vancouver Pigeon Patrol / Bird Control / Surrey Pigeon Control / Pest / Vancouver Pigeon Blog / Birds Inside Home / Pigeons in the cities / Ice Pigeons





/am-tree-sparrow-58ca9fc73df78c3c4f9a3610-5a0e0f3a9e942700377f9e72.jpg)





